SRE is what you get when you treat operations as if it’s a software problem. This field originated at Google and spread into the broader software development industry, and other companies subsequently began to employ site reliability engineers. Organizations who have adopted the concept include Airbnb, Dropbox, IBM, LinkedIn, Netflix and Wikimedia.
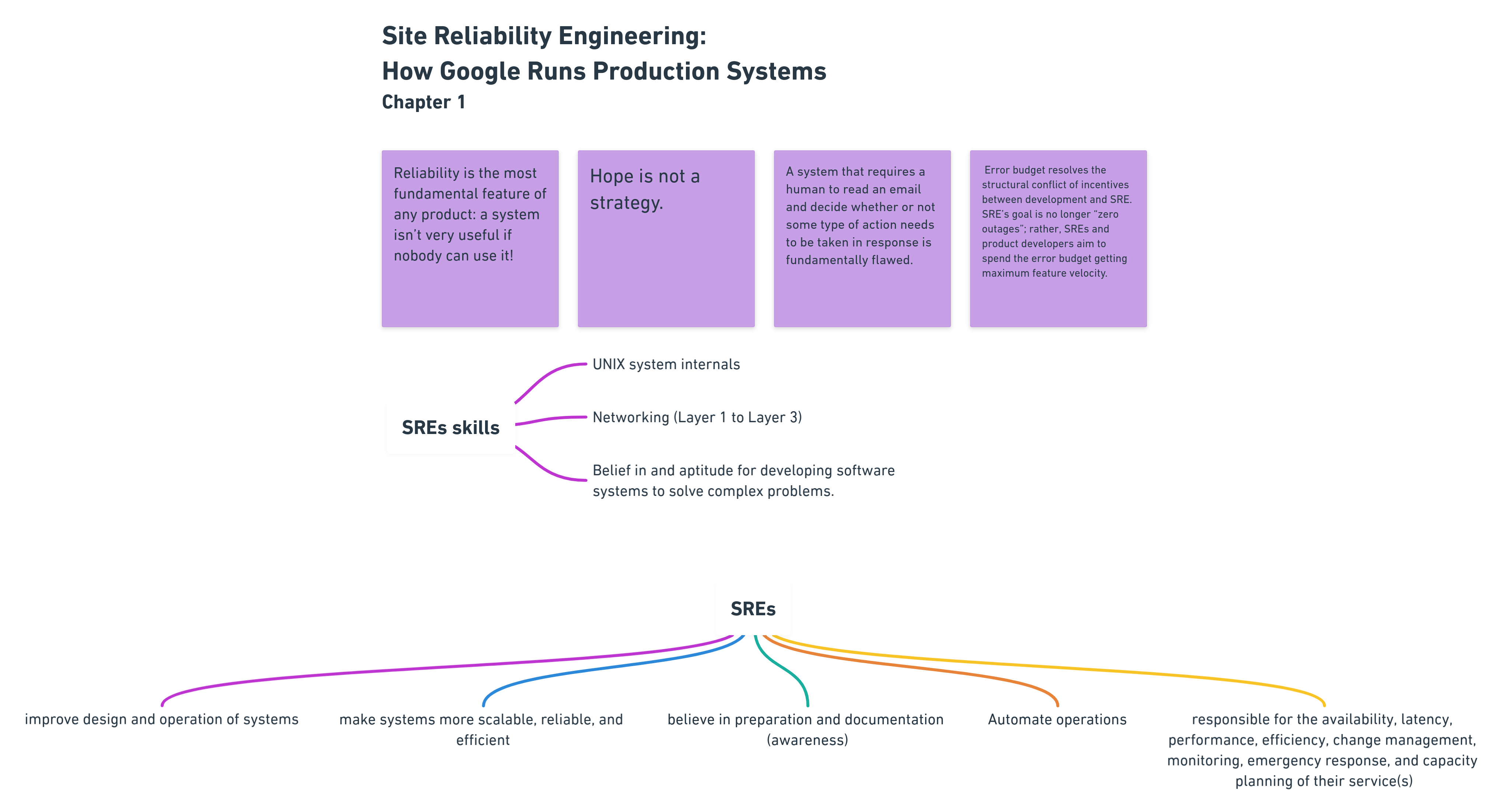
Reliability is the most fundamental feature of any product. It doesn’t matter to have a great product if customers can’t use it.
The problem with reliability originates with the separation between software and operations, teams started to engage in a silent battle to advance their interests. The ops team attempts to safeguard the running system against the risk of change by introducing launch and change gates. The dev team responds by having fewer “launches”, “feature toggles”, “incremental updates”, “cherrypicks”, to avoid the launch review. None of these actions really prevents outages or even delivers more value to users.
SRE uses the concept of error budgets to solve this conflict, by balancing innovation (new features) with stability. SRE’s goal is no longer “zero outages”; rather, SREs and product developers aim to spend the error budget getting maximum feature velocity.
SREs responsibilities include:
- Improve design and operation of systems
- Make systems more scalable, reliable, and efficient
- Automate operations
- In general responsible for: availability, latency, performance, efficiency, change management, monitoring, emergency response, and capacity planning of their service(s)